With BP/Statoil in Nigeria

When their partnership began in 1991, the two companies became involved in the Democratic republic of the Congo as well as Angola and Nigeria, but withdrew from the first of these areas in the same year. A venture in Equatorial Guinea, operated from Nigeria, was also short-lived.[REMOVE]Fotnote: Ryggvik, Helge. (2009). Til siste dråpe. Oslo: Aschehoug: 238.
Through various engagements, BP was already established in all three west African states when the alliance with Statoil began. However, the military regime in Nigeria had taken over the British oil major’s operations in the country during 1979 as part of a massive nationalisation wave. During the 1990s, the Nigerian mood shifted from nationalisation to internationalisation, and a more open attitude was adopted towards foreign companies. That change in climate created an opening for BP to return to the giant of Africa, this time accompanied by Statoil.
Repressive regimes, executions and environmental disasters
Statoil was to be responsible for the alliance’s joint operations in Nigeria, making this country its baptism of fire as an international oil company. A significant proportion of the staff intended to support these activities were located in Stavanger. But a number of BP personnel were included in this Norway-based Nigeria management from the start.[REMOVE]Fotnote: Ryggvik, Helge. (2009). Til siste dråpe. Oslo: Aschehoug: 231
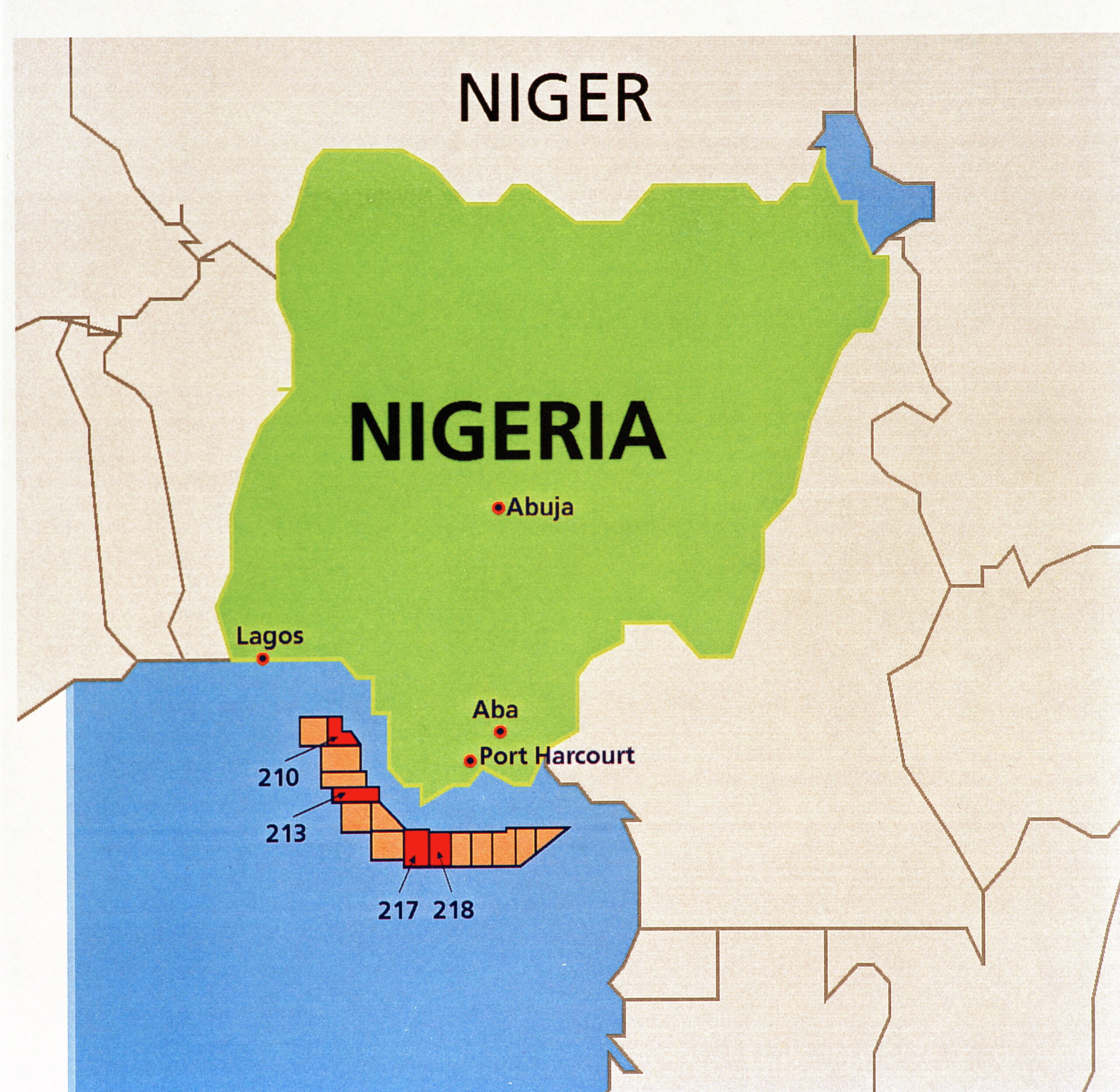
Operational responsibility for the west African commitment was allocated to BP and its London head office. Only a minimal share of alliance personnel were permanently stationed in Africa. While 23 people, all BP employees, worked with Angola from London, only one was based full-time in Luanda. Thirty staff handled Nigeria in Stavanger, with a single person in the African country itself.
Nigeria remained an important priority area until the mid-1990s, and activity there expanded. The alliance succeeded with its strategy and established itself as a leading player in the deepwater areas off the Nigerian coast. That position was completely overturned in 1995, when political conditions in Nigeria deteriorated dramatically.
Ever greater dissatisfaction had spread among many of the people living around the Niger delta. They received little or no share of the big revenues generated by the oil resources in their region. In addition, a massive environmental disaster began to manifest itself in the delta area.
A coup in 1993 had introduced one of the most brutal and corrupt regimes in Nigeria’s history. The repressive government banned all political activity and opponents were jailed. That in turn unleashed extensive protests across much of the country. These increased from 1995 after the military regime executed nine activists from the oil-rich delta – including author and environmental activist Ken Saro-Wiwa.
These executions helped to create pressure from international public opinion. Foreign companies faced demands to pull out of Nigeria. The worst-affected was Shell, which had been producing oil for many years from a controversial part of the Nigeria delta. But organised campaigns were also conducted against Statoil in Norway. The company responded that it did not want to become involved in political processes and chose to accept the political burden of remaining in Nigeria. It argued that the human rights position would not improve if it and BP withdrew.

These developments were not particularly concerning for the alliance to begin with. It concentrated on offshore exploration, and was not involved with oil spills and dead fish in the delta. And, in the middle of the unrest on land, the alliance could raise a mighty cheer when oil was proven with its first wildcat – which also represented the first deepwater discovery off Nigeria. But the jubilation was short-lived, since the resources proved non-commercial. At the same time, the political conditions caught up with the partners.
Statoil had the most to lose by pulling out. Nigeria was where the company intended to demonstrate that it could serve as an operator, even under difficult conditions, outside the North Sea.
It now transpired that repressive regimes, executions and environmental disasters were not the only problems facing BP and Statoil. The financial difficulties were a more difficult challenge. Nor had the alliance succeeded in securing its own operatorships. And its interests in other fields had also failed to yield sufficient oil to justify the exploration costs. The accounts were looking critical.[REMOVE]Fotnote: Ryggvik, Helge. (2009). Til siste dråpe. Oslo: Aschehoug: 233.

No big breakthrough occurred on the exploration side. On 20 April 1998, Statoil and BP signed a contract with Nigerian company Allied Energy on the sale of the alliance’s 40 per cent interest in block 210 – the Oyo oil field. It afterwards transpired that neither Statoil nor BP received the sale price. In addition came a price reduction of about 30 per cent, which many have characterised as incomprehensible.[REMOVE]Fotnote: Keilen, Erlend. (2003. 3. november). E24. Statoil fikk aldri betalt for oljefelt i Nigeria
An investigation was conducted, and its report concluded in 2004 that: the fact that the statements obtained are ambiguous, combined with the fact that no written documentation exists about the decisions which must have been taken, provides some scope for speculation. On that basis, the investigation committee would recommend to Statoil that it conducts an internal inquiry to clarify the circumstances. The following day, Statoil declared itself not guilty of corruption at a press conference in Oslo.[REMOVE]Fotnote: E24. (2010. 1. mars). NTB. Hemmelig Statoil-gransking av priskutt i Nigeria.
Although the alliance itself withdrew from Nigeria, Statoil remained on an independent basis and had interests in 2020 in Agbami – the country’s largest deepwater field.
Chevron is the operator of the field with a 67.30 percent ownership interest and Prime 127 has the remaining 12.49 percent. Equinor also operates two exploration licenses – OML 128 and 129 – with a share of 53.85 per cent in both. Six wells have been drilled in both, with two discoveries made. None of the fields are planned developed.
On Equinor’s own website, the company describes that its success in Nigeria “is underpinned by our sustainability work, ensuring we are a responsible operator and are proactive in improving opportunities for the communities where we work.”[REMOVE]Fotnote: https://www.equinor.com/where-we-are/nigeria
